
- OPENGL 2.0 DRIVER WINDOWS 10 MANUALS
- OPENGL 2.0 DRIVER WINDOWS 10 SOFTWARE LICENSE
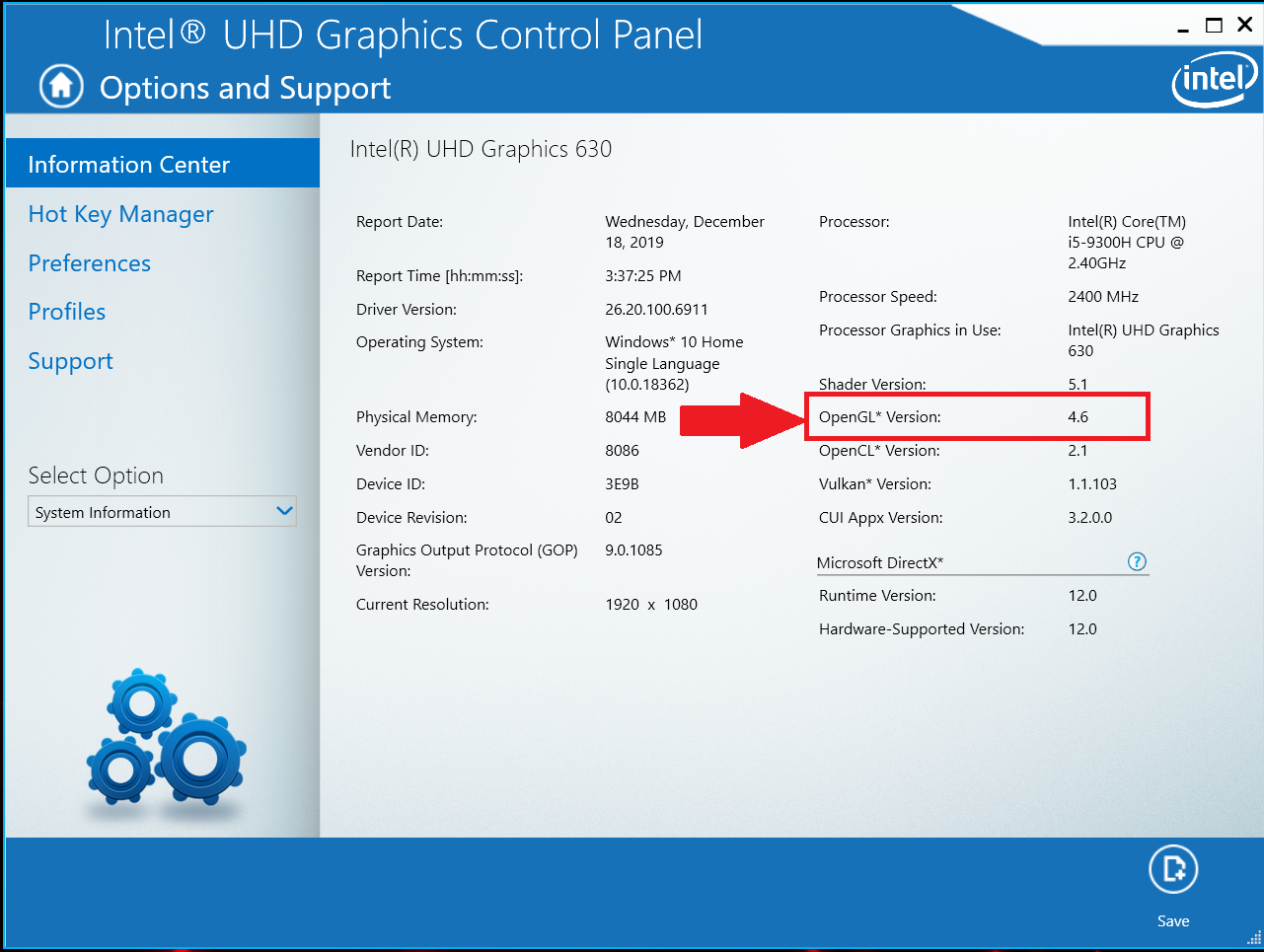
- OPENGL 2.0 DRIVER WINDOWS 10 MANUAL
- OPENGL 2.0 DRIVER WINDOWS 10 LICENSE
Includes a poster-sized fold-out diagram showing the structure of an idealised OpenGL implementation.
OPENGL 2.0 DRIVER WINDOWS 10 MANUAL
ISBN 3-X Essentially a hard-copy printout of the Unix manual (man) pages for OpenGL. The Blue Book OpenGL Reference manual, 4th edition. ISBN 978-9-8 A book about X11 interfacing and OpenGL Utility Toolkit (GLUT). The Green Book OpenGL Programming for the X Window System. ISBN 3-1 A tutorial and reference book for GLSL. ISBN 978-9-1 The Official Guide to Learning OpenGL, Version 4.5 with SPIR-V The Orange Book OpenGL Shading Language, 3rd edition. The Red Book OpenGL Programming Guide, 9th Edition. These are commonly referred to by the colors of their covers:
OPENGL 2.0 DRIVER WINDOWS 10 MANUALS
The OpenGL Architecture Review Board released a series of manuals along with the specification which have been updated to track changes in the API.

The features introduced by each new version of OpenGL are typically formed from the combined features of several widely implemented extensions, especially extensions of type ARB or EXT. In such cases, it could also happen that the Khronos Group's Architecture Review Board gives the extension their explicit approval, in which case the identifier ARB is used. If multiple vendors agree to implement the same functionality using the same API, a shared extension may be released, using the identifier EXT. For example, Nvidia's identifier is NV, which is part of the extension name GL_NV_half_float, the constant GL_HALF_FLOAT_NV, and the function glVertex2hNV(). Įach extension is associated with a short identifier, based on the name of the company which developed it. All extensions are collected in, and defined by, the OpenGL Registry. Vendors can use extensions to expose custom APIs without needing support from other vendors or the Khronos Group as a whole, which greatly increases the flexibility of OpenGL. Extensions may introduce new functions and new constants, and may relax or remove restrictions on existing OpenGL functions. In addition to the features required by the core API, graphics processing unit (GPU) vendors may provide additional functionality in the form of extensions. The details of each version are decided by consensus between the Group's members, including graphics card manufacturers, operating system designers, and general technology companies such as Mozilla and Google. New versions of the OpenGL specifications are regularly released by the Khronos Group, each of which extends the API to support various new features. For the same reason, OpenGL is purely concerned with rendering, providing no APIs related to input, audio, or windowing.

The specification says nothing on the subject of obtaining, and managing an OpenGL context, leaving this as a detail of the underlying windowing system. In addition to being language-independent, OpenGL is also cross-platform. As such, OpenGL has many language bindings, some of the most noteworthy being the JavaScript binding WebGL (API, based on OpenGL ES 2.0, for 3D rendering from within a web browser) the C bindings WGL, GLX and CGL the C binding provided by iOS and the Java and C bindings provided by Android. Although the function definitions are superficially similar to those of the programming language C, they are language-independent. The API is defined as a set of functions which may be called by the client program, alongside a set of named integer constants (for example, the constant GL_TEXTURE_2D, which corresponds to the decimal number 3553). Although it is possible for the API to be implemented entirely in software, it is designed to be implemented mostly or entirely in hardware. The OpenGL specification describes an abstract API for drawing 2D and 3D graphics. Īn illustration of the graphics pipeline process Since 2006, OpenGL has been managed by the non-profit technology consortium Khronos Group. (SGI) began developing OpenGL in 1991 and released it on Japplications use it extensively in the fields of computer-aided design (CAD), virtual reality, scientific visualization, information visualization, flight simulation, and video games. The API is typically used to interact with a graphics processing unit (GPU), to achieve hardware-accelerated rendering. OpenGL ( Open Graphics Library ) is a cross-language, cross-platform application programming interface (API) for rendering 2D and 3D vector graphics.
OPENGL 2.0 DRIVER WINDOWS 10 LICENSE
OPENGL 2.0 DRIVER WINDOWS 10 SOFTWARE LICENSE
: This is a Free Software License B closely modeled on BSD, X, and Mozilla licenses.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
